Unraveling the Potential of Data Fabric: A Cutting-Edge Paradigm in Pharma Data and Analytics
Introduction
The life sciences industry is at the forefront of generating an unprecedented volume and diversity of data, leading the data landscape to rapidly expand from genomics and clinical trials to real-world patient data and wearables. As life sciences organizations create more and more applications and data sets, the data becomes increasingly siloed and inaccessible for use beyond its initial scope. This wealth of information holds immense promise for personalized medicine, precision treatments, and accelerated drug discovery. However, with the exponential growth of data, the challenges associated with managing, maintaining, securing, and governing it have also escalated substantially. What follows is a discussion of the importance of a data fabric and its potential to be the cornerstone of success for life sciences companies.
What is a Data Fabric?
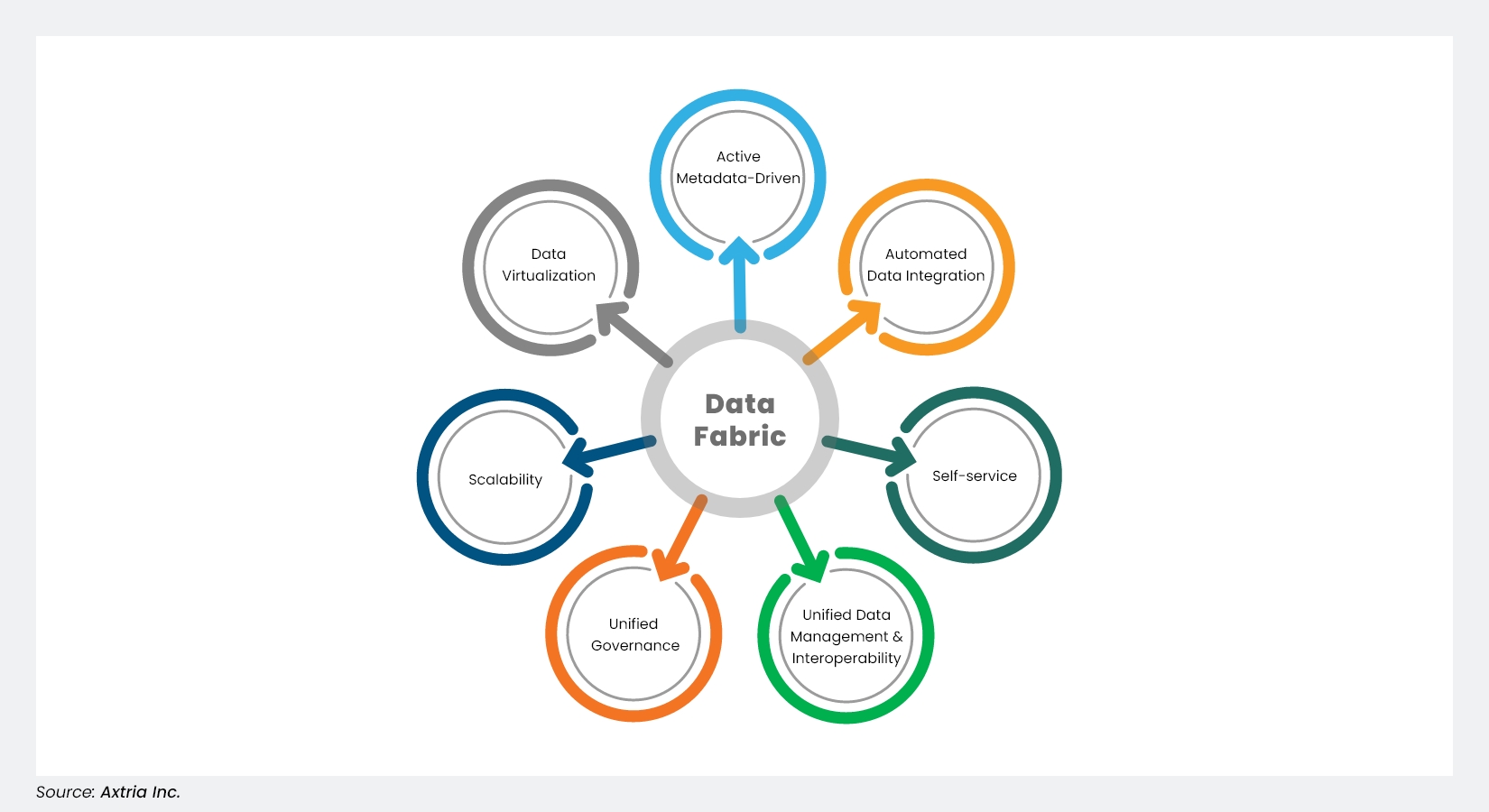 Figure 1: The core components of a data fabric
Figure 1: The core components of a data fabric
As IBM defines it, a data fabric is an architecture that weaves different environments and pipelines together by using intelligent and automated systems or processes.1 It helps organizations manage and maximize the value of their data. By using a data fabric, organizations can reduce the time it takes to collate and clean data, freeing up time for value-added tasks such as data analysis and interpretation. And in the new era of artificial intelligence (AI), data is becoming even more important for life science organizations – from drug discovery to commercialization.
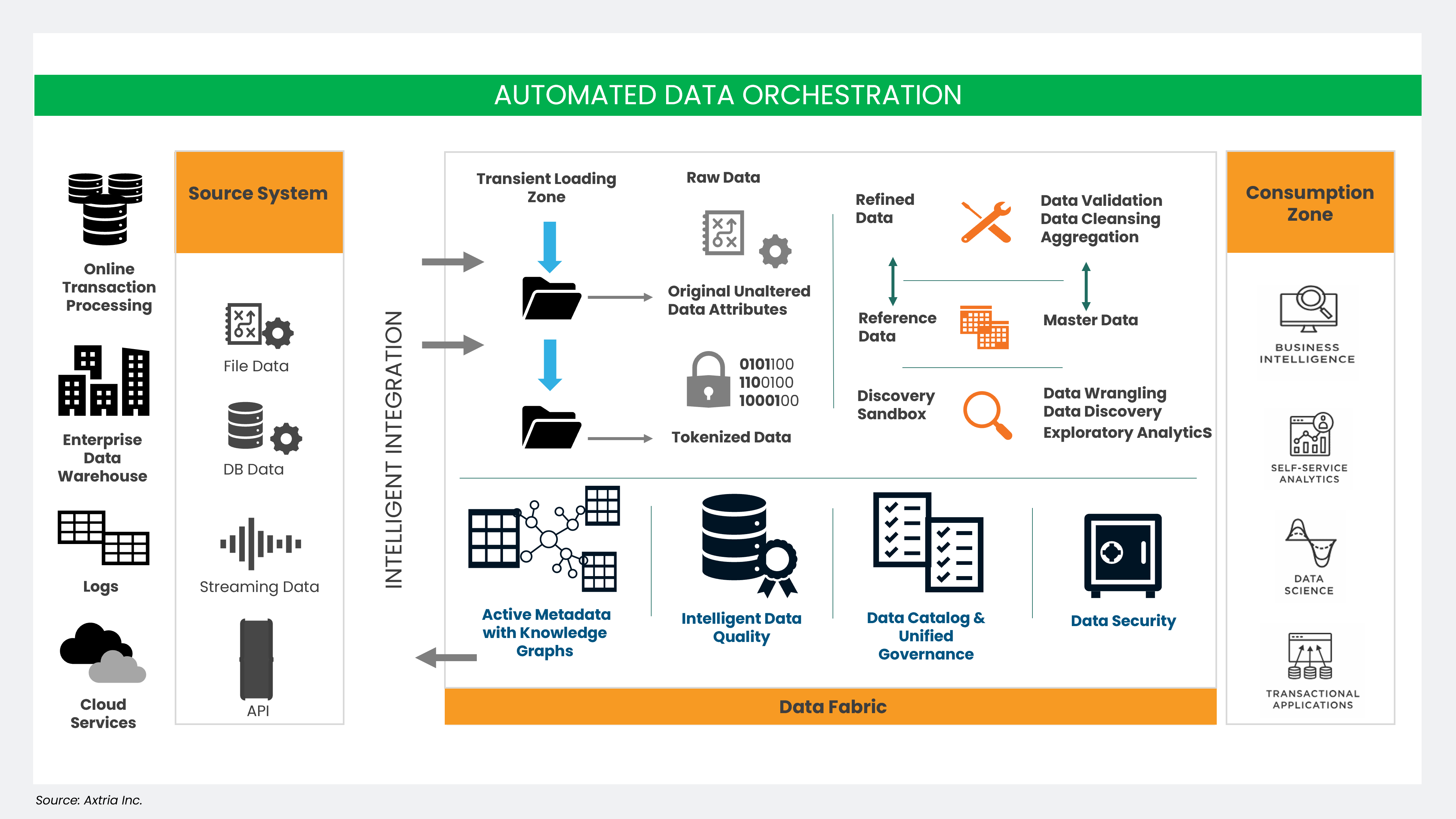 Figure 2: Detailed architecture of a data fabric
Figure 2: Detailed architecture of a data fabric
Value Proposition
 Figure 3: Benefits at enterprise scale
Figure 3: Benefits at enterprise scale
The fundamental function of data fabric is to integrate data from various sources, formats, and locations, providing a centralized and consistent data management approach for various business functions. For life sciences organizations specifically, a data fabric enables the seamless combination of patient and provider information from an array of sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), sales data, marketing data, real-world evidence, and more. This ecosystem provides a unified view of critical information, fostering interoperability and enhancing data-driven decision-making. Some of the specific life sciences use cases for a data fabric include the following:
Real-world Evidence Integration: A data fabric bridges the gap between clinical trial data and real-world evidence. This coalescence enhances post-market surveillance, supports regulatory submissions, and strengthens the case for drug efficacy and safety, instilling confidence in customers and regulatory authorities.
Targeted Marketing and Sales Strategies: With a unified view of customer data—including physician prescribing patterns, patient demographics, and sales performance—a data fabric empowers pharma companies to create targeted sales and marketing strategies, optimizing engagement and increasing market share.
Personalized Customer Engagement: A data fabric's ability to unite patient and physician data gives pharmaceutical companies unified customer insights and enables reps to have personalized interaction with healthcare professionals. Tailored engagement leads to stronger customer relationships and improved patient adherence.
Improved Market Insights: A data fabric makes it easier to analyze market trends, competitor intelligence, and customer preferences. By leveraging these insights, pharma companies can identify new market opportunities and adjust their commercial strategies accordingly. By breaking down data silos, a data fabric also reduces the risk of using inconsistent or outdated information.
Scalability and Flexibility: Data fabrics scale easily with an organization’s growing data requirements. Pharmaceutical companies generate and consume vast quantities of information – not just the number of prescriptions written, or units sold, but hard-to-quantify data like social media posts and online engagements, coupled with the treasure trove of information in real-world evidence. Uncovering the insights held in all this data has never been more critical. A data fabric ensures that the infrastructure can adapt and grow to harness the power of this diverse data landscape.
Challenges with Implementation and Adoption
There are several risks to consider when adopting a data fabric, but none of these is a showstopper. Each one is surmountable if careful—and correct—actions are taken. Here are the biggest stumbling blocks during data fabric implementation:
Legacy System Compatibility: Integrating a data fabric into legacy systems can be arduous. These pre-existing systems may lack the necessary application programming interfaces (APIs) or data formats required for seamless integration. If your legacy system falls in this category, it will require additional development efforts and potential system upgrades.
Data Quality: A data fabric relies on accurate and high-quality data to deliver meaningful insights. Ensuring quality, establishing governance policies, and enforcing standards are essential to avoid data inconsistencies and errors.
Cost and Resource Investment: Implementing a data fabric requires a dedicated financial investment in infrastructure, technology, and skilled resources. Organizations need to weigh the costs of a data fabric against the expected benefits to ensure a positive return on investment.
Vendor and Technology Selection: Selecting the right data fabric vendor and the technology that aligns with an organization's needs can be a gargantuan task. Evaluating the available options, conducting proof-of-concept tests, and negotiating contracts require careful consideration.
Change Management and Adoption: Implementing a data fabric may require organizational changes and adjustments to existing processes. Gaining buy-in from stakeholders, training employees on the new system, and ensuring a smooth transition are critical for successful adoption.
Cultural Shifts: Alongside change management, be aware that implementing a data fabric may require a cultural shift in the organization. It may call for a new focus on data-driven decision-making with collaboration across departments. Resistance to change and siloed approaches can hinder successful adoption.
Notable Players in the Data Fabric Space
The critical aspect of any data management journey is providing a complete view of the data. There are some players in the market today that can help. While a talented team can build a data fabric on various cloud-based vendors, some offerings are touted as “turnkey” solutions.
Microsoft Fabric2 is emerging as a leader in the data fabric space. It is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering with unified analytics. Microsoft Fabric combines four major features: product experience, compute and storage, governance and security, and a business model.
SAP Data Intelligence Cloud and SAP Datasphere3 are solutions that encourage innovation with data. They provide batch and real-time data processing, self-service, data discovery, governance, and more to enable quicker decision-making. They can integrate and orchestrate massive data volumes and streams at scale.
Conclusion
Data fabric is a game-changer for life sciences organizations, unlocking the full potential of data and artificial intelligence to drive business growth, market competitiveness, and customer satisfaction. By integrating diverse data sources, enabling real-time access, and supporting advanced analytics, a data fabric empowers pharmaceutical companies to make informed decisions, enhance customer engagement, and optimize operations, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes and patient care.
REFERENCES
- IBM. What is a data fabric? Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.ibm.com/topics/data-fabric
- Microsoft. Microsoft Fabric. Accessed September 12, 2023.https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/
- SAP. SAP Datasphere enables a business data fabric. SAP Datasphere Features. 2023. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.sap.com/products/technology-platform/datasphere/features.html#business-data-fabric
Author details

Bilahari Manipuzha
Bilahari has 17 years of expertise in conceiving and constructing data integration and analytics platforms tailored specifically for the life sciences. His unique blend of deep domain knowledge, complemented by his exceptional technical proficiency, has played a pivotal role in aiding global enterprises in the development of cutting-edge analytics solutions.

Rajeev Bhardwaj
Rajeev is a Solutions Architect with the Axtria Technology Center of Excellence team. His expertise spans generative AI, large language models, Big Data engineering, business information management, cloud computing, and advanced analytics.




