Comparing Predictive Models: Traditional Versus Modern Statistical Approaches for Economic Outcomes in Major Depressive Disorder
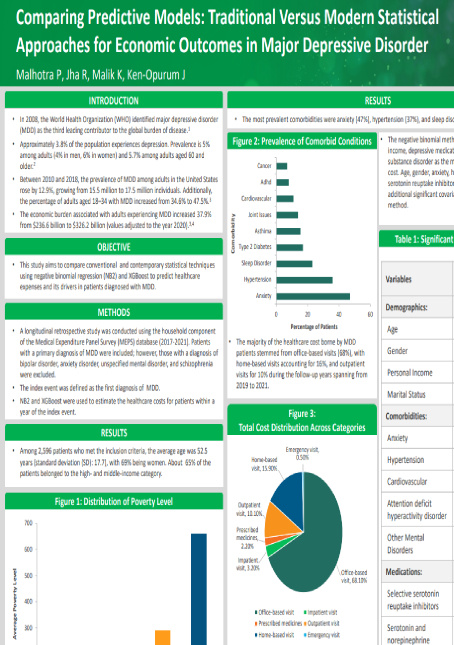
In 2008, the WHO identified major depressive disorder (MDD) as the third leading contributor to the global burden of disease. About 3.8% of the global population experiences depression, with a prevalence of 5% among adults and 5.7% among those aged 60 and older. From 2010 to 2018, MDD prevalence in U.S. adults rose by 12.9%, from 15.5 million to 17.5 million, particularly among those aged 18–34. The economic burden of MDD increased by 37.9%, from $236.6 billion to $326.2 billion (2020 values). This study compares negative binomial regression (NB2) and XGBoost to predict healthcare expenses for MDD patients using the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) database (2017-2021). The study included 2,596 MDD patients, excluding those with other mental disorders. The average patient age was 52.5 years, 69% were women, and 65% were from high- and middle-income categories.
This report is a poster presentation of Axtria from ISPOR 2024.
Contact us at connect@axtria.com with any questions.
Recommended insights

White Paper

Case Study