Transforming Pharma With ChatGPT: Exploring The Future Of Sales, Marketing, And Customer Experience

So, I asked ChatGPT to write me a joke about a pharma sales rep who walks into a bar.
ChatGPT: A pharmaceutical sales rep walks into a bar and asks the bartender, "What's the cure for a bad day?" The bartender responds, "I don't know, but I bet you have a pill for it."
All jokes aside, ChatGPT has many valuable use cases in life sciences. From drug discovery to patient engagement, ChatGPT can assist researchers in various ways to accelerate their research and improve the quality of their findings. Let's dive into the details of how ChatGPT can be used in life sciences.
What is ChatGPT?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in the life sciences industry has grown rapidly in recent years. One of the most promising areas of AI in commercial life sciences is Generative AI technology, such as the ChatGPT model. ChatGPT, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is a machine learning model that has been trained on a vast body of text data to generate human-like responses to text prompts. OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, says the latest version (GPT-4) is significantly larger and more powerful than its predecessors.1 Version 3.0 had 175 billion parameters. While OpenAI has not publicly revealed how many are in Version 4, some reports place it at one trillion2, while others claim it is as much as 170 trillion3. This massive increase in size allows GPT-4 to process and generate text more accurately and fluently.4 While GPT-3.5 is limited to producing responses of approximately 3,000 words, GPT-4 can generate responses exceeding 25,000 words.5 Compared to its predecessor, GPT-4 has an 82% lower likelihood of responding to requests for prohibited content and scores 40% higher on certain standardized tests (e.g., SAT®, United States Medical Licensing Examination®, Law School Admission Test, and more). In another advancement, GPT-4 can also summarize and comment on images and complicated texts.
Azure OpenAI comprises models grouped by family and capabilities; a model family is typically organized by its intended task. Furthermore, the alphabetical order of the models generally represents the capability and cost. For example, GPT-3 models use the following names: Ada, Babbage, Curie, and Davinci.
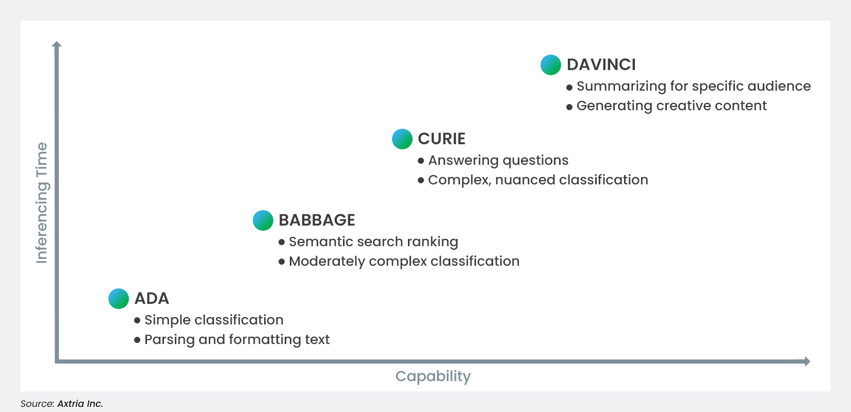
Figure 1: ChatGPT has more Models—A, B, C, D—with increased capability and complexity from A to D.
Industry Adoption
With recent advancements in the capability and accuracy of the underlying model used in ChatGPT, there has been a significant increase in adoption in the industry. There are also models trained with domain-specific data, like BioGPT, a domain-specific Generative Transformer language model pre-trained on large-scale biomedical literature tasks.6 Doximity, a digital platform for medical professionals, rolled out a beta version of a ChatGPT tool, DocsGPT, for doctors.7 It helps streamline time-consuming administrative tasks like drafting and faxing preauthorizations and appeal letters to insurers. Also, Microsoft recently announced the availability of ChatGPT in Azure. This will accelerate the adoption of ChatGPT because of Azure’s enhanced data security guardrails, especially in heavily regulated industries such as life sciences.
As shown in Figure 2 below, Axtria is integrating GPT models into our products. For example, Axtria DataMAx™ is already using GPT technology to drive efficiency and bring significant productivity gains to our customers.
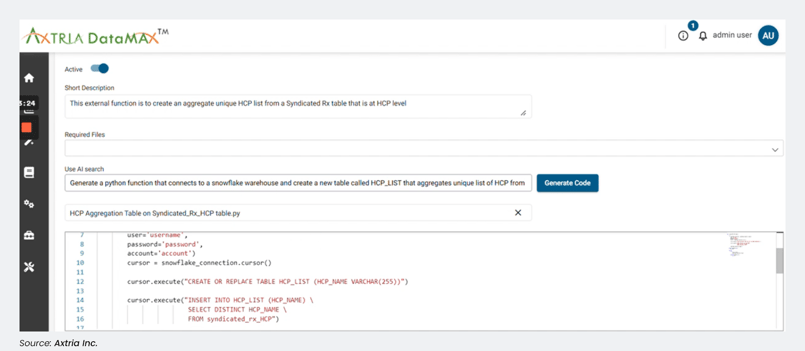
Figure 2: Axtria DataMAx™ using GPT models for code generation.
Use Cases in Pharma
ChatGPT can be applied in various ways to improve efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making in the life sciences industry. Some ChatGPT use cases in life sciences are outlined in Figure 3 below:
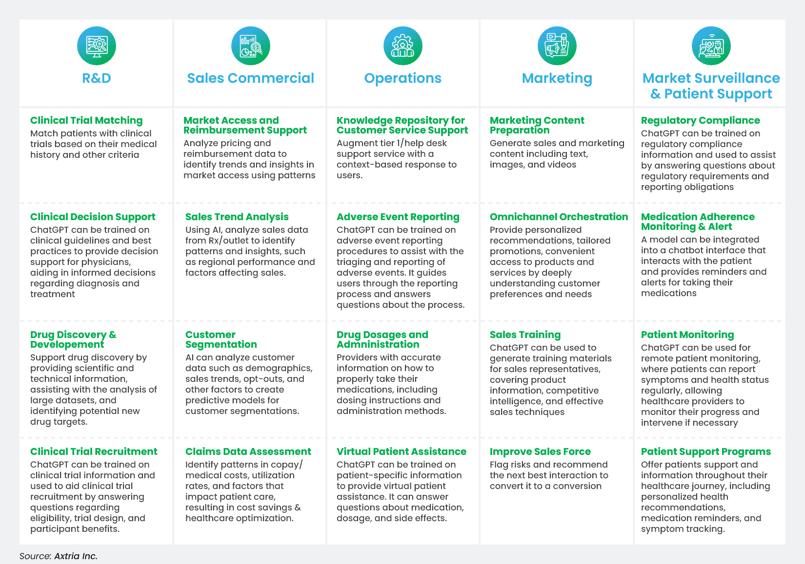
Figure 3: Business use cases across various life sciences value chains.
In addition to the use cases mentioned earlier, there exist numerous possibilities for ChatGPT's further applications. Let's explore some of the use cases in greater detail below.
Drug Discovery and Development: Pharmaceutical research and development is one area where ChatGPT could be very helpful. Pharma companies spend billions of dollars every year developing new drugs, and the process can take years or even decades. ChatGPT will be able to generate hypotheses about new drug targets after parsing through research papers, clinical trial results, and patent applications, potentially saving researchers time and resources by suggesting new avenues to explore. The architecture below represents the implementation approach in an Azure ecosystem for this use case.8
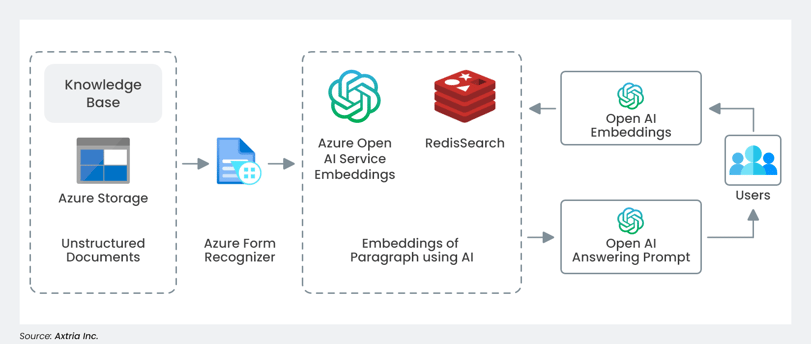
Figure 4: A reference architecture to harness research papers, clinical trial data, and patent applications.
Personalized Medicine: Personalized medicine involves tailoring medical treatments to an individual's genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. ChatGPT can analyze large datasets of patient information to generate insights about the best treatments for specific patients, helping healthcare providers deliver more effective therapies, and reduce the risk of adverse drug reactions.
Patient Engagement and Adherence: Chatbots powered by GPT can provide patients with tailored support, answering questions and providing guidance based on the patient's unique needs. Because of this, patients better understand their medical conditions and treatments, leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life. This technology provides a customized experience and enhances therapy effectiveness.
Sales and Marketing: ChatGPT can facilitate sales and marketing efforts in the life sciences industry by analyzing healthcare professionals’ (HCP) prescribing patterns, preferences, and opinions about drugs. ChatGPT’s analysis capabilities can also help companies develop more effective digital marketing strategies and help field reps provide real-time information to HCPs, engage with patients, and improve sales and patient outcomes. Its context-specific information enhances the quality of field reps’ interaction with HCPs. The architecture shown below represents the implementation approach in the Azure ecosystem for this use case.9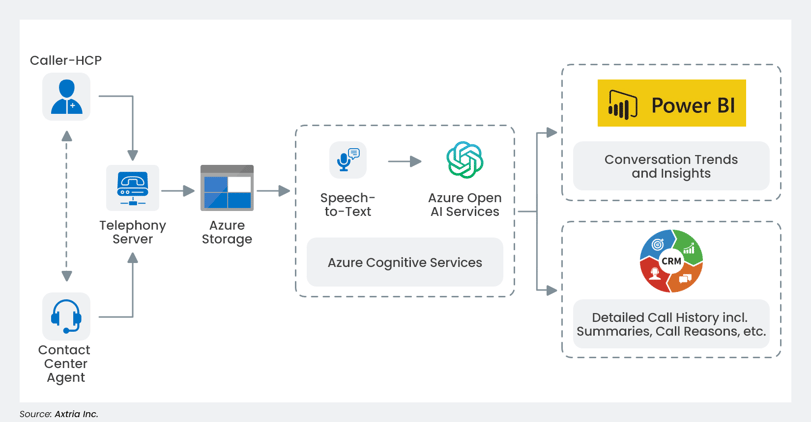
Figure 5: Reference architecture for generating insights and leads from contact center calls.
Clinical Trials: ChatGPT can analyze and interpret data from clinical trials, including patient data, lab results, and medical images, helping researchers identify patterns and trends that might be missed by traditional statistical analysis. ChatGPT can also generate patient recruitment materials and informed consent forms in multiple languages to improve patient enrollment and retention.
Regulatory Compliance: ChatGPT can also assist companies in complying with regulatory requirements related to drug development and marketing by analyzing regulatory guidelines and generating reports that demonstrate compliance with these guidelines. ChatGPT can also assist with adverse event reporting and labeling requirements.
Challenges
When using ChatGPT in the field of life sciences, there are additional cautions and challenges to consider due to the complexity and sensitivity of the data being used and its potential impact. Figure 6 below shows four major areas that need to be considered when using ChatGPT capabilities.
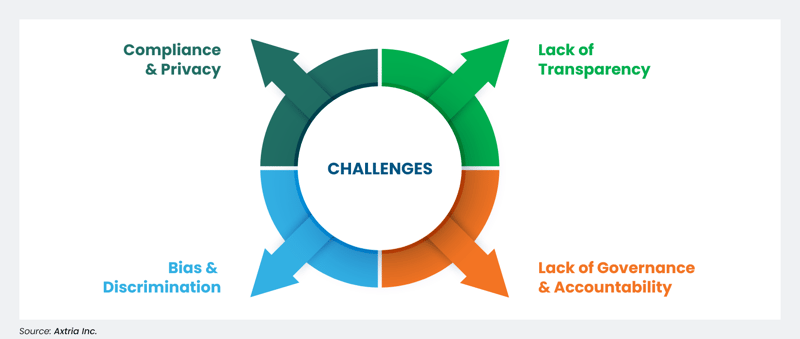
Figure 6: Considerations of usage of ChatGPT in life sciences.
One of the most significant of these is ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information generated by the chatbot. It is essential to train the chatbot on high-quality data and incorporate feedback mechanisms that allow users to correct and refine the chatbot's responses.
Another challenge for using GPT in life sciences is ensuring patient privacy and data security. We must protect patient data from unauthorized access and disclosure by designing chatbots to comply with applicable laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
ChatGPT also raises ethical considerations, particularly around issues of bias and transparency. A key problem is the data itself may have racial bias that needs to be mitigated. Large language models like ChatGPT reflect and perpetuate the structural inequalities on the biased data and algorithms. So, it is essential to ensure that data used to train algorithms is diverse and representative, and that algorithms are regularly audited for bias. We must ensure that the model is transparent in its decision-making processes and does not perpetuate biases that could harm patients or contribute to health disparities. Black box models, unclear training data and decision-making processes, and lack of accountability can limit trust and confidence, impacting their suitability for use in certain applications. A careful assessment should be performed on the use cases to ensure these challenges are addressed.
While there are challenges in the broader usage of language models in the life sciences, the potential near-term benefits are enormous and exciting. As technology advances, we can expect language models to become even more valuable tools for pharmaceutical companies, ultimately leading to better support for HCPs and patients, and improved health outcomes around the world.
References
- OpenAI Research. Research index [Internet]. San Francisco: OpenAI; 2023 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://openai.com/research
- Bastian M. GPT-4 has a trillion parameters – report [Internet]. Utrecht (The Netherlands): Decoder; 2023 Mar 25 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from:https://the-decoder.com/gpt-4-has-a-trillion-parameters/
- Lubbad M. The ultimate guide to GPT-4 parameters: everything you need to know about NLP’s game-changer [Internet]. San Francisco: Medium; 2023 Mar 19 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://medium.com/@mlubbad/the-ultimate-guide-to-gpt-4-parameters-everything-you-need-to-know-about-nlps-game-changer-109b8767855a
- Heaven WD. GPT-4 is bigger and better than ChatGPT—but OpenAI won’t say why [Internet]. Cambridge: MIT Technology Review; 2023 Mar 14 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/03/14/1069823/gpt-4-is-bigger-and-better-chatgpt-openai/
- Bushwick S. What the new GPT-4 AI can do [Internet]. New York: Scientific American; 2023 Mar 16 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/what-the-new-gpt-4-ai-can-do/
- Luo R, Sun L, Xia Y, Qin T, Zhang S, Poon H, et al. BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining [Internet]. Redmond (WA): Microsoft Research; 2022 Nov [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/biogpt-generative-pre-trained-transformer-for-biomedical-text-generation-and-mining/
- Doximity. DocsGPT [Internet]. San Francisco: Doximity [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.doximity.com/docs-gpt
- Microsoft. Extract text from objects using Power Automate and AI Builder [Internet]. Redmond (WA): Microsoft Corporation [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/example-scenario/ai/extract-object-text
- Microsoft. Use a speech-to-text transcription pipeline to analyze recorded conversations [Internet]. Redmond (WA): Microsoft Corporation [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/example-scenario/ai/speech-to-text-transcription-analytics
Author details

Vipin Tyagi
Vipin has 20+ years of IT experience, with more than 14 years in the Data warehousing and Business Intelligence area. Expertise includes client engagement, delivery management, project/program management, for key accounts. Proven track record in delivery of strategic programs, including architecture, design, development, implementation, integration and IT enabled transformation of enterprise application systems. He has rich experience in pharma commercial area such as Sales and Marketing, Clinical, trial operations and finance.

Bilahari Manipuzha
Bilahari had 15 years of experience in designing and building Data Integration and Analytic platforms for Life Science and Healthcare customers. With domain knowledge coupled with technical expertise, he has helped various global organizations to build Analytics Platform and solutions in public clouds, on-premises, and hybrid to address the business needs.




