Innovation And Industry Perspective: Master Data Management
What is Master Data Management?
Master Data Management (MDM) is a data management discipline wherein core business dimensions are maintained and governed by people (the data governance organization) and processes to ensure up-to-date, accurate, and quality data. These dimensions, also called MDM domains, can include products, customers, and suppliers, just to name a few.
Master Data Management is often the initial focus for any organization’s data strategy, as it impacts the accuracy of every business transaction conducted at the intersection of two or more dimensions. For example, a sale is conducted at the intersection of customer and product, while procurement is at the intersection of supplier and product. Master data quality creates a snowball effect on the quality of business transactions, which impacts business analyses to drive strategic and tactical business decisions. Poor quality of the master data leads to poor business decisions.
Specialized technical solutions called MDM platforms facilitate master data management. According to Market Research Future, the MDM market size is expected to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 16.9% by 2030.1
MDM Technology Industry Trends
Axtria expects several factors to drive the adoption of MDM technologies and services, including the rising need for compliance, cloud transformation, and an increasing trend toward managing multiple domains. In this article we identify six related industry trends that will have a considerable influence on MDM platforms’ next-generation evolution, and Master Data Management adoption over the next few years.
-
Leverage of AI/ML
Artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) Solution is evolving rapidly, turning data management into intelligent data management. MDM platforms are applying AI/ML to accelerate the delivery of quality master data for consumption by enterprise solutions and business users, leading to operational efficiency across information technology (IT) and the wider business. Some of the prevalent AI/ML use cases in MDM (Master Data Management) orchestration include:-
Data acquisition: Onboarding a new data source and mapping it to a master data model has traditionally been a manual effort. Now, AI/ML techniques, such as named entity recognition (NER) and natural language understanding (NLU), are used to automate the identification of fields and field types when mapping them to master data models.
-
Data quality issue prevention: Beyond traditional, simple, attribute-level data quality checks, AI/ML makes it possible to detect complex, context-based relative data quality anomalies automatically.
-
Data classification: With digital transformation and increasing privacy and compliance requirements, it is mandatory to classify data. This can include categories like personal information (PI) and the broader personally identifiable information (PII). AI/ML makes it possible to automatically classify data at an enterprise scale, which may not be feasible with manual human effort at an enterprise scale.
-
Data matching: A primary feature of MDM Solutions is matching profiles across various internal enterprise and third-party data sources, yielding higher data quality by merging duplicated entries. MDM solutions are progressing towards orchestrating AI/ML in data matching instead of traditional, rule-based data matching.
-
Transforming unstructured data: With digital data being a new source to enrich master data, a variety of unstructured data is now being integrated into Master Data Management. Applying AI/ML in a pre-MDM layer to parse and extract structured attributes is another area where AI/ML helps exploit value from digital data.
-
-
Cloud Transformation
Today’s digital era, with petabytes of data, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and omnichannel customer reach, has been the catalyst for cloud transformation. Speed, flexibility, scalability, high availability, and seamless integration with other cloud-based systems are now the inevitable requirements for any business to survive. Creating such applications at a cost-effective price point has been a primary reason why next-gen MDM platforms and solutions are being deployed on the cloud as Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings. The life sciences industry has been an early adopter of Master Data Management solutions, especially for its customers: the healthcare providers (HCPs) and healthcare organizations (HCOs). As such, most life sciences clients are either in the middle of evaluating MDM SaaS platforms and planning a transformation or have already started their transformation journey to MDM SaaS. -
Customer/Patient Experience (CX/PX) Management
Another growing trend is the focus on an omnichannel experience for HCPs (CX – customer experience) and patients (PX – patient experience). The need for CX and the phasing out of third-party cookies have shifted the focus to first-party data. This has led to the extension of Master Data Management solutions to integrate with digital channels, enabling the creation of customer 360 and patient 360. While customer MDM and customer 360 have been prevalent for years for HCP/HCO analytics, this PX trend has led to the exploration of patient MDM for enabling advanced patient analytics. Broadly speaking, life sciences clients have either implemented novice patient MDM use cases, are exploring the feasibility of advanced use cases, or they are in a strategy planning phase of patient MDM.CX/PX is also one of the key drivers leading MDM platforms to incorporate advanced integration capabilities, such as application programming interface (API) and real-time data streaming integration, enabling the holistic 360 view.
-
Privacy, Data Residency, and Security
Compliance and regulatory requirements constantly evolve to provide privacy, data protection, and mitigate security breaches. That means privacy, data residency, and security management are increasingly becoming integral parts of every data management platform, including MDM platforms, to ensure adherence to regulations and avoid penalties. -
Multi-domain
While the life sciences industry traditionally started with managing the customer domain (HCP/HCO/affiliations), it has evolved over the past ten years and now encompasses other domains, particularly:-
Product domain – for various business requirements, such as market basket creation, market share analysis, and Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP) compliance.
-
Supplier domain – for overall supply chain efficiency, as well as for enabling supply chain vigilance (the effect of supply chain disruption due to COVID-19) to ensure the safety of the products and services.
-
Sites domain – a prevalent domain for clinical data management. From the MDM SaaS platform perspective, the out-of-the-box capabilities are still at their beginning stage. Nevertheless, this domain is getting attention and is expected to evolve over the next few years to enable clinical data management use cases centered on data quality and analytics requirements for sites, investigators, and clinical trials.
MDM platforms have advanced capabilities that cater to multi-domain data management requirements. These capabilities extend the platforms’ use beyond the primary go-to-market domain and simplify business analytics, enabling management and visualization of cross-domain relationships.
-
-
Global Solution vs. Regional/Local
MDM solutions have traditionally been implemented at a function level, such as one for commercial and another for R&D/clinical, or different solutions by regions/countries. Clients have started to realize the benefits of standardization and are migrating to one global MDM platform, breaking functional and geographical barriers. These migrations generally happen alongside other transformational initiatives, such as one customer relationship management (CRM) solution or one enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution. This trend also leads to Master Data Management transformation initiatives, which are not just a lift-and-shift approach to move to one MDM technology. Instead, it is a strategy and tactic to transform MDM functions and operations, leveraging next-gen capabilities and embracing a cloud-first approach.Summary View of How Industry Trends are Leading to Next-gen MDM
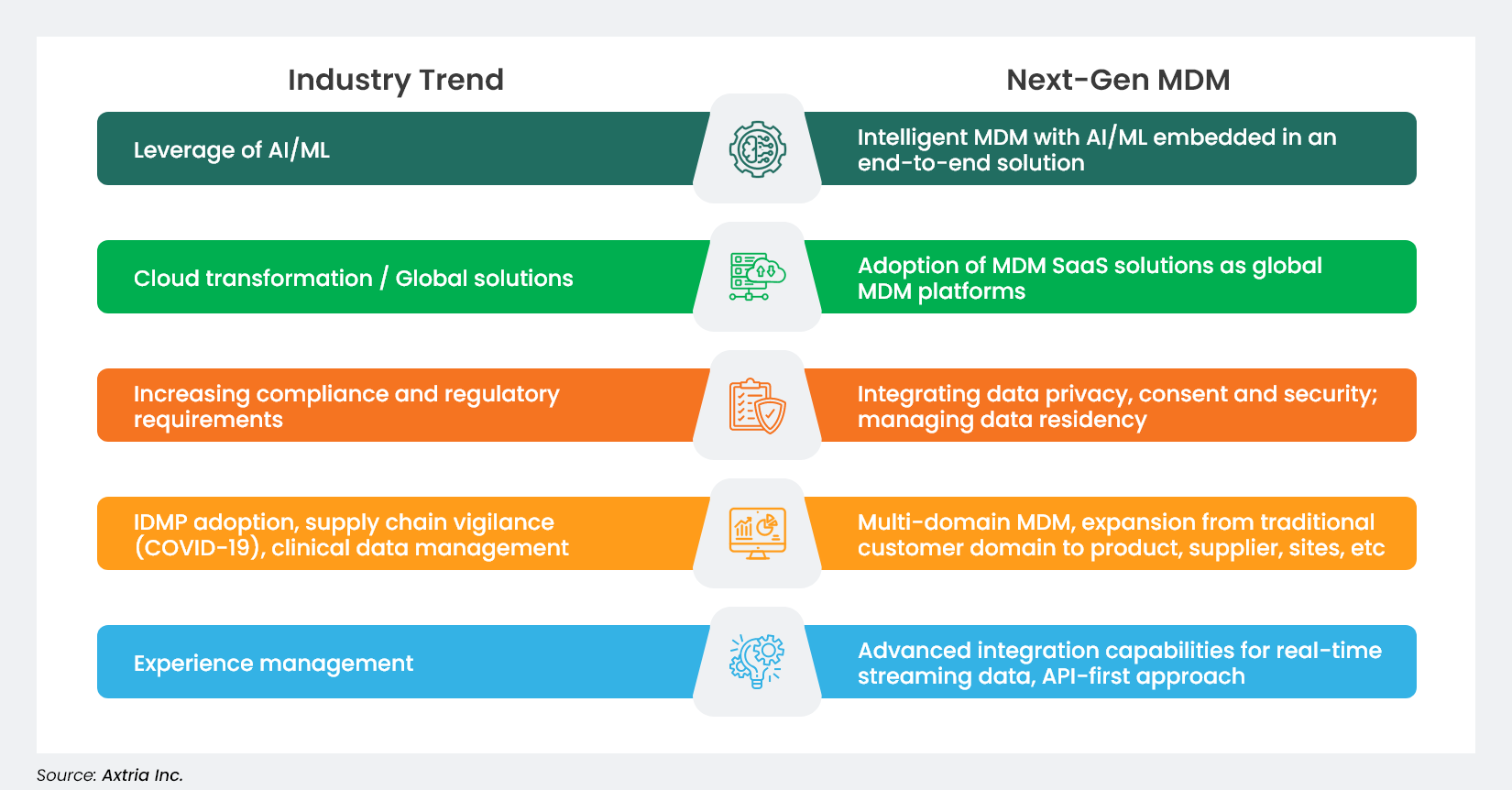
Conclusion
There is no shortage of reasons why a company needs a MDM solution. The sheer volume of available data makes that a necessity right now. But the emerging trends described here show that a traditional solution may no longer meet today’s needs. The rapid advancement of AI/ML, the renewed focus on CXs, the plethora of regulations, and the expansion of domains all point to the need for a next-generation Master Data Management answer. It needs to be robust and, perhaps above all, scalable; not only to handle the trends described here but also for the industry changes we know will inevitably arrive.
References
- Dhapte A. Master data management market research report. Market Research Future. May 2023. Accessed May 31, 2023. https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/master-data-management-market-6723
Author details

Harneet Kapil
Principal, Business Information Management, Axtria. Harneet is a Principal with Axtria. She is a senior technology leader who successfully supports health science and retail data management, and analytics functions. She is a logical thinker and continuous learner, noted for providing innovative solutions to complex business problems. Harneet possesses in-depth knowledge of industry-relevant business processes, data assets, tools, and technologies. She is a data management specialist with extensive experience in defining and executing data strategy and delivery of enterprise-wide data capabilities, focusing on a sustainable data architecture that supports business agility.




