Omnichannel Marketing
Introduction
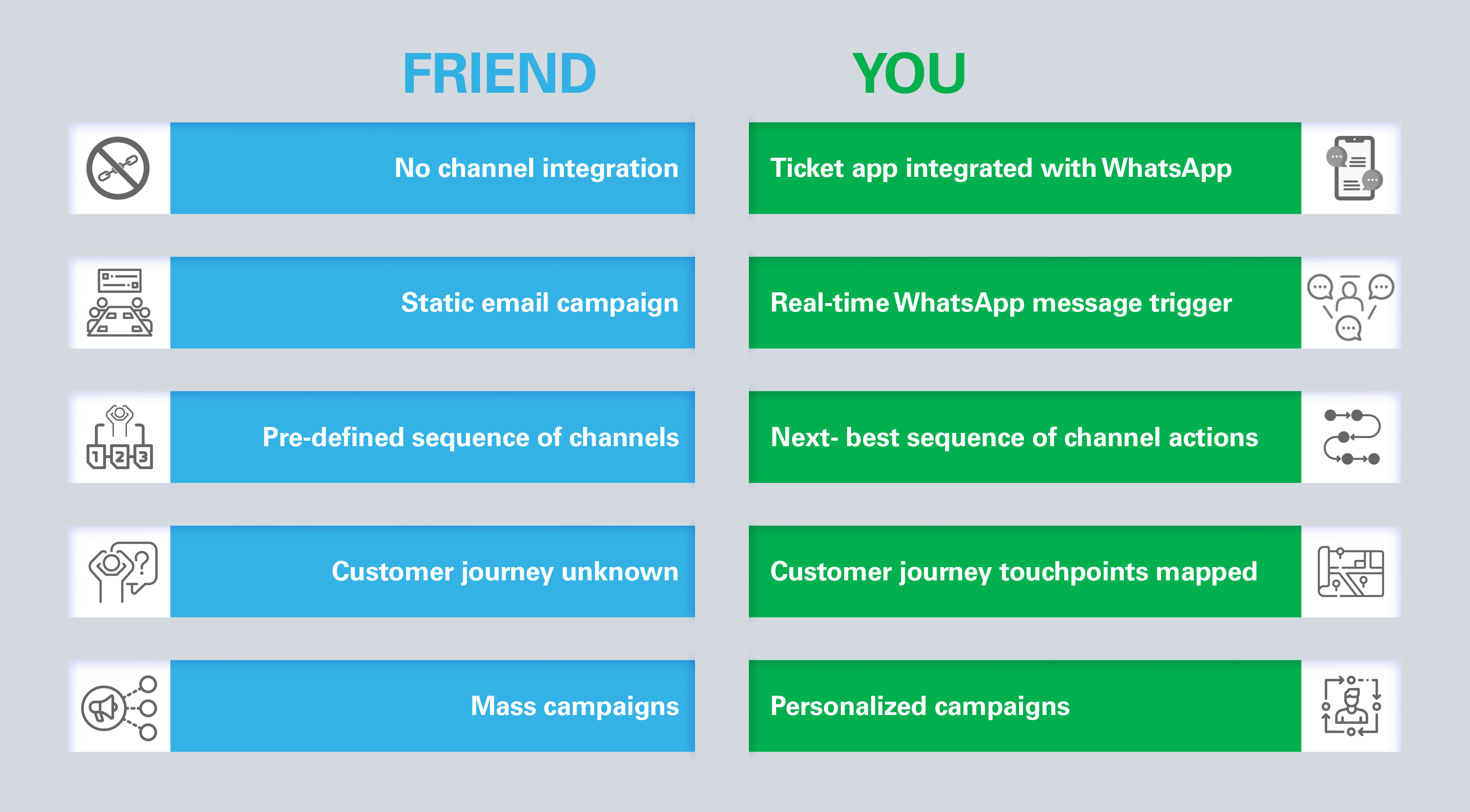
Imagine you and a friend are checking the price of an IMAX movie ticket on two different movie ticket apps. You both find the tickets expensive and choose not to purchase them through either app.
A minute after deleting the items in your cart, you receive a WhatsApp message from the first ticket app. Based on your cart history, the app sends you a link offering a 30% discount on your order. In contrast, your friend receives a regular email from the other app a few hours later. It contains a generic discount code with no obvious connection to their cart history or reference to the app visit.
What was the difference between the two scenarios?
While you both received a promotion, your friend’s coupon sent hours later was far less effective than the personalized offer you received in real-time via your preferred channel (in this example, WhatsApp) at a price point with a high likelihood of acceptance (in this example, a 30% discount).
The two scenarios mentioned above are simple but powerful illustrations of the increased impact of omnichannel marketing compared to a single-channel promotion.
What Is Omnichannel Marketing?
Omnichannel marketing is designed to provide customers with highly personalized, well-optimized experiences for each touchpoint and journey stage. An omnichannel implementation allows companies to leverage channels across all divisions (marketing, sales, service, commerce, etc.) and determine the most impactful engagement tactic based on each customer’s previous interaction. The concept leverages business rules and machine learning models to generate insights from that history to decide the most effective channel, message, and cadence combination for reaching each target customer with a winning offer.
Differences Between Omnichannel, Multichannel, and Cross-channel Marketing
Companies have been targeting customers through multiple channels for years, so what are the differences between marketing methods? Let us compare the terminology to understand precisely how omnichannel is different.
- Multichannel Marketing: Multiple marketing channels (sales, marketing, service, commerce, etc.) execute static, time-bound marketing campaigns.
- Cross-channel Marketing: Channels are integrated and promoted based on customer events rather than focusing on one brand campaign.
- Omnichannel Marketing: Decisioning is applied at each customer touchpoint through real-time, intelligent, next-best actions. This method produces the most personalized option—a highly impactful, enhanced experience for target customers.
The graph below compares key variables across the three marketing frameworks:
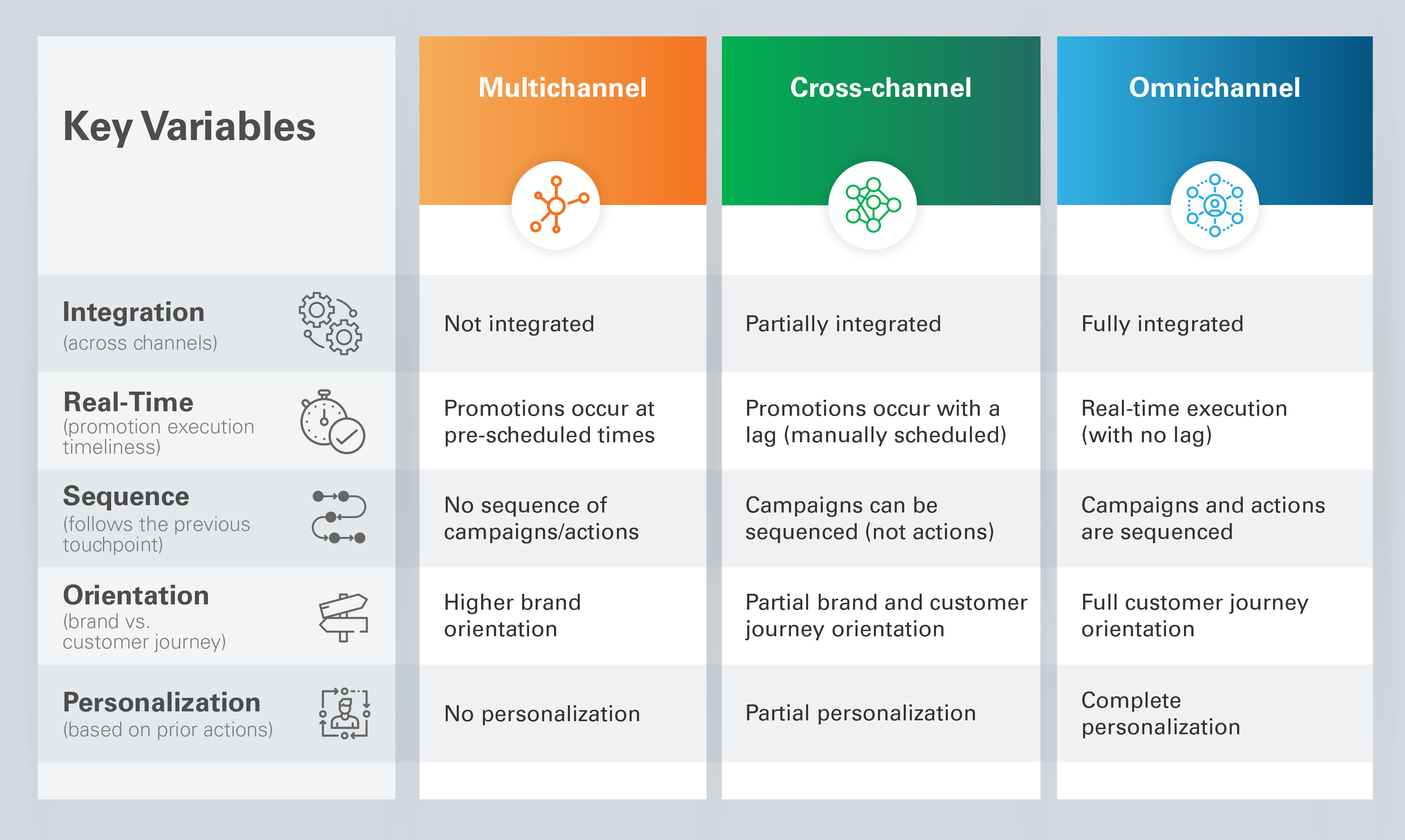
With this in mind, let’s revisit the example of the ticket-purchasing app. It is now clear that while your friend was targeted with a multichannel marketing campaign, you were luckier to be targeted with an omnichannel marketing campaign. Below is a summary of the differences between these approaches:
Importance and Benefits of Omnichannel Marketing
- What Can Omnichannel Do?
- Enhance Customer Experience: Before omnichannel’s emergence, customers received messages that were not always relevant to the context of the current customer journey stage. These messages were delivered across several static channels and often missed important touchpoints. Omnichannel marketing is ground-breaking in providing seamless, contextual, and highly integrated experiences across all customer touchpoints. Omnichannel execution drives agile and intelligent content that responds to customer actions in the most timely and engaging manner and the channels most relevant to the customer journey.
- Create a Custom-made, Integrated Channel Experience: Multichannel marketing cannot provide an integrated channel experience in real-time through the next best channels. Omnichannel marketing ensures relevant channel touchpoints are deployed at critical moments in each stage of a customer’s journey for optimal channel engagement.
- Improve Personalization: The most valuable characteristics of any omnichannel program are its ability to put each customer journey step in context and provide personalized interactions based on historical preferences. Omnichannel’s deployment of complex rules and machine learning models helps set up the framework for meaningful personalization.
- Deliver a Cohesive Brand Strategy: Adherence to a brand's strategic goals and objectives can be difficult to review when executing multichannel campaigns. Omnichannel marketing helps ensure that all channel and tactic implementations align with the brand strategy, vision, and overarching communication objectives.
- Measurable Results of Using Omnichannel
- Higher Engagement: The most crucial benefit of omnichannel marketing is its ability to increase engagement across the customer’s most preferred channel.
- Increased Revenue: Sharing marketing messages in the interaction types most likely to convert helps increase revenue at each customer journey stage.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: A customer is most satisfied if there is a seamless progression along the right channels to complete their objectives. Omnichannel supports customer satisfaction at each interaction, thus increasing brand loyalty.
- Better Attribution Data: One of omnichannel marketing’s benefits is that it helps marketers improve their attribution data, allowing them to understand better how customers interact with their brand and make more informed decisions in the future.
- Greater Reach and Less Churn: With the right channels, content, and cadence, companies can increase customer reach and reduce churn, resulting in greater adherence to journey completion.
Key Execution Challenges and the Need for an Omnichannel Framework
With this understanding of omnichannel marketing, its importance, and key benefits, let us look at the key roles needed for omnichannel execution.
- Data Analysts manage and integrate customer data across all possible channels. A data profiler supports key data management activities, including data collection, storage, data model management, and infrastructure maintenance.
- Brand/Sales Managers review and map customer journey stages to identify the right touchpoints for sharing omnichannel messages. They may belong to multiple promotional teams and are jointly responsible for developing a customer journey.
- Data Scientists are responsible for developing a library of models that can be deployed to generate omnichannel next-best actions. They are involved in model generation, maintaining the repository, updating models, and other tasks.
- Operations Analysts deploy omnichannel actions based on program goals for overall impact. This profile is responsible for activating omnichannel triggers and actions and reviewing pre-defined metrics for success.
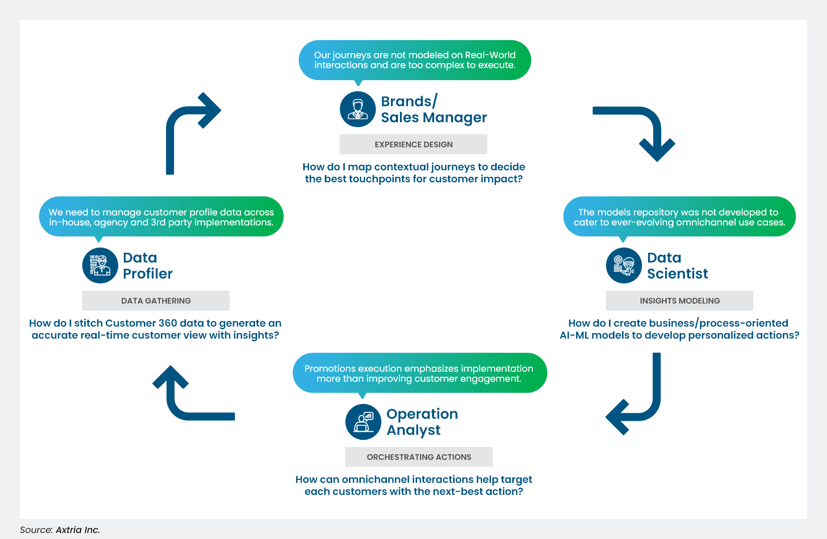
Figure 1: Role-specific Execution Challenges
Omnichannel Marketing: Implementation Framework
A standard omnichannel marketing strategy can apply to any organization in any industry. It must include the following key components:
- Single Customer View: Gather Customer 360 data to generate insights for every customer. This stage identifies all available customer data sources and integrates the data at each customer touchpoint.
- Map the Customer Journey: Review customer journey stages to reveal the common paths of key customer personas and identify their touchpoints across each path.
- Personalized Actions: Customer + Channel + Content = 3C: Deploy a mix of 3C-integrated attributes to design and develop contextual actions specific to each customer based on their historical interactions.
- Orchestration and Measurement: Activate actions and measure the impact of each one. Optimize offers based on individual customer responses to each request. This stage involves real-time interaction across customer journey touchpoints to activate the most effective next best action.
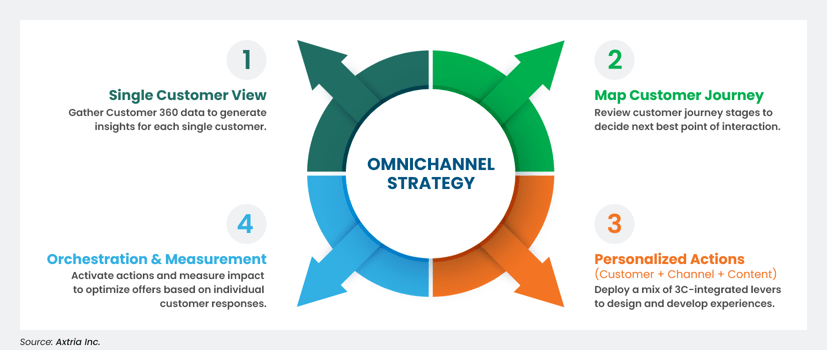
Figure 2: Omnichannel Marketing Strategy Framework
Creating a Perfect Customer Experience with Omnichannel Marketing
Companies that implement the four-step omnichannel strategy can improve the customer experience by focusing on four key levers:
- Customer Intelligence: Generates target-level insights through Customer 360 and a single customer view application, helping develop the highest level of customer intelligence to support the creation of the most impactful omnichannel actions.
- Customer Impact: Persona-based customer journey mapping can help omnichannel teams identify which decision touchpoints will significantly impact the customer journey.
- Customer Engagement: Delivers contextual actions to customers, improving the overall promotional impact across any channel (sales, marketing, customer service) based upon the choice of any 3C combination.
- Customer Value: Monitors Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to enhance customer value based on feedback for each omnichannel action. Well-thought-out KPIs help optimize the next best steps in each iteration for maximum value.
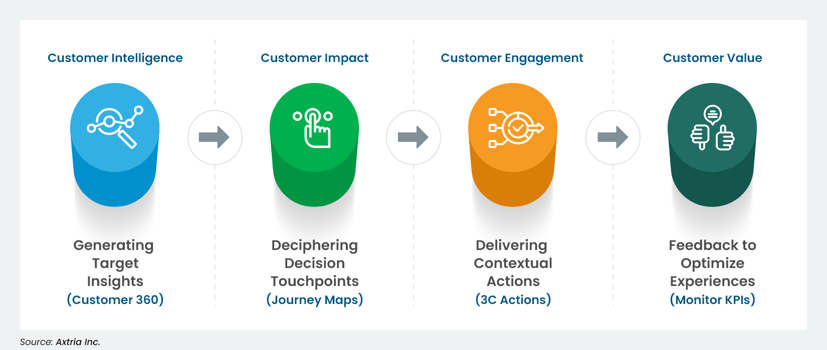
Figure 3: Levers of Customer Experience
Omnichannel Campaign Execution: Key Considerations
Setting up an omnichannel campaign requires intense planning and execution capabilities. Key steps in building omnichannel campaigns include:
- Invest in Solid Data Management Capabilities: Creating a Customer 360 view at an individual level is only possible with reliable data management. Companies must be willing to invest in data management to develop the right platform and tool ecosystem to successfully collect, store, manage, and process data across multiple sources. Most omnichannel implementations include in-house and enterprise tools, including data warehouses, data storage, customer data platforms, data management platforms, data lakes, and privacy management solutions. Companies can either build a stack of standalone tools or invest in integrated platforms that leverage the best of custom and standard industry features.
- Build Personas and Customer Journeys: This stage involves developing personas and customer journeys to understand which channels and touchpoints are the most logical targets for omnichannel campaigns. Teams can leverage various persona- and journey-management tools to establish ongoing and predictive journeys for omnichannel implementation.
- Determining Inputs for the Decisioning Engine: The next stage for developing a campaign involves deciding on the customer, channel, and content (the 3Cs) for execution. This decision-making process uses data from the established data management ecosystem and customer journeys. Steps in this process include:
- Filter target customers based on omnichannel use cases.
- Decide on channels for activation of filtered targets.
- Leverage available content types across chosen channels.
- Generate and Activate Next-best actions: The “decision engine” takes in finalized 3C inputs and applies business rules and machine learning models to generate the next best actions. These actions are then activated as campaigns across multiple omnichannel tools, such as marketing, sales, service, and commerce. These campaigns are monitored for budget, pacing, response, and other factors.
- Review and Optimize Experiences: Finally, the impact of omnichannel campaign actions is monitored regularly according to pre-defined metrics. Omnichannel use cases, the 3Cs, KPIs, and other elements should all be revisited based on customer adoption and feedback to improve the overall value and provide a seamless customer experience.
Omnichannel Marketing in Life Sciences and Healthcare
The inception of omnichannel marketing can be traced back to its roots in retail and e-commerce, where it initially aimed to enhance conversion rates. Since then, this innovative approach has transcended into various sectors, catalyzing the acceleration of digital adoption. Notably, amidst the widespread impact of COVID-19, the healthcare and life sciences domains have emerged as frontrunners in embracing digital transformation and wholeheartedly embracing the omnichannel marketing strategy.
Key use cases for omnichannel in life sciences and healthcare include:
- Improving Patient Care: Omnichannel insights and actions help brands understand key patient pain points across their patient journey. By leveraging Patient 360 data, healthcare companies now have insights across key personas to activate effective real-time campaigns and offer the best support in patient assistance programs, co-pay card activations, in-treatment care support, and house visits at the time of need, among other initiatives.
- Accelerating Drug Sales: A life sciences company’s key priority is to influence different target profiles, including patients, doctors, nurses, or pharmacies. This happens at each stage of a drug promotion during a brand’s life cycle, from launch through growth to loss of exclusivity (LoE).
- Physicians and Hospital Support: Omnichannel marketing has had a substantial impact on generating insights that influence key healthcare stakeholders, including doctors and hospitals. These insights improve the overall brand portfolio’s efficacy, safety, affordability, and access.
Key Takeaways
Omnichannel marketing is becoming one of today’s most actionable marketing trends. The ability to track each customer’s journey and target them with personalized, data-driven offers has many applications across industries. While multiple commercial groups like sales, marketing, customer service, and others follow their own specified goals, the time has come to use each latent interaction across established channels as a potential trigger for actions across business units. Companies can now target customers with predictive next best actions in real-time, thanks to advances in data, technology, and marketing tools. Testing and investing in multiple use cases across key personas is the best way to realize the benefits of an omnichannel approach.
Organizational alignment is often seen as a critical impediment to omnichannel success. But once companies integrate their teams, resources, and investments, omnichannel will undoubtedly be seen as a worthy revenue generator and the most critical driver of customer experience.
Very soon, we will get real-time, meaningful, personalized offers on each activity we conduct online or offline. Returning to the ticket purchasing example at the beginning of our discussion, you will know that real omnichannel marketing has arrived when you and your friend start receiving undeniably the next best offers at the prices most agreeable to you and the app.
This article was contributed to by Puneet Bhatia, Senior Director at Axtria.
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Omnichannel Marketing?
- Differences Between Omnichannel, Multichannel, and Cross-channel Marketing
- Importance and Benefits of Omnichannel Marketing
- Key Execution Challenges and the Need for an Omnichannel Framework
- Omnichannel Marketing: Implementation Framework
- Creating a Perfect Customer Experience with Omnichannel Marketing
- Omnichannel Campaign Execution: Key Considerations
- Omnichannel Marketing in Life Sciences and Healthcare
- Key Takeaways



